India’s Healthcare Sector: A Transformative Infrastructure Expansion
India’s healthcare sector accelerates growth with massive investments, new hospital beds, advanced diagnostics, and stronger urban-rural medical infrastructure.
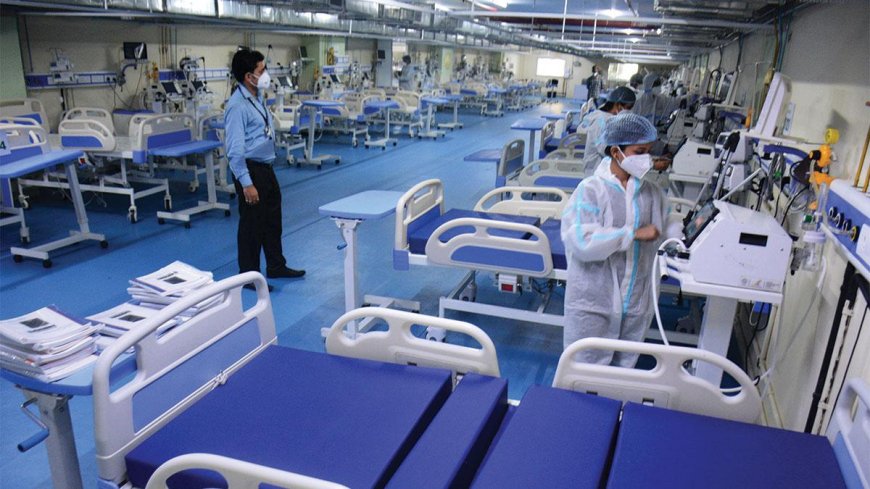

India’s healthcare sector is undergoing a transformative expansion, with a major push to upgrade hospital infrastructure across both urban and rural regions. This ambitious growth is driven by rising healthcare demand, government policy support, and substantial private sector investments. The sector is witnessing the introduction of new intensive care units (ICUs), emergency care units, and advanced diagnostic facilities, ensuring better access to high-quality medical care for millions of Indians.
Scale of Expansion
The expansion is taking place at an unprecedented scale. Industry estimates indicate that the private sector alone will add over 34,000 new hospital beds by 2028–29, requiring an investment of approximately ₹40,000 crore.
This growth is concentrated in North and South India, with Tier-II and Tier-III cities accounting for nearly 40% of the new capacity, signaling a deliberate effort to bridge the urban-rural healthcare divide.
Major hospital chains leading the expansion include:
-
Apollo Hospitals – planning to add 3,512 beds in phases across Pune, Kolkata, Hyderabad, Gurugram, Chennai, Varanasi, Mumbai, and Lucknow.
-
Max Healthcare – expanding its capacity across key metros.
-
Artemis Hospitals – aiming to double its bed strength, focusing on Delhi-NCR and select Tier-II cities in North India.
Government Initiatives
The Union Budget 2025–26 has allocated nearly ₹1 lakh crore to healthcare, with substantial funding dedicated to:
-
Building district-level cancer centres
-
Strengthening primary and critical care infrastructure under the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission
The government is also implementing innovative strategies such as:
-
Digital twin-based planning for infrastructure and asset management
-
Surge-ready hospital layouts to handle future health emergencies
These initiatives aim to build a resilient, future-ready healthcare system.
Addressing Urban and Rural Gaps
While metropolitan regions are seeing rapid upgrades, the expansion is equally focused on underserved areas. Government-led district cancer centres and hospital upgrades aim to:
-
Reduce the load on urban hospitals
-
Improve equitable access to healthcare
Private players are also expanding into Tier-II and Tier-III cities, driven by rising health awareness and growing demand post-pandemic.
Advanced Diagnostic Facilities
The expansion goes far beyond increasing bed capacity. Hospitals are integrating advanced diagnostic technologies, including:
-
State-of-the-art imaging systems
-
Laboratory automation
-
AI-driven diagnostic tools
These advancements improve the speed and accuracy of disease detection and treatment—crucial for managing complex cases and emergencies.
Impact on Healthcare Access and Quality
The sector-wide upgrade is expected to:
-
Enhance healthcare access
-
Improve treatment quality and outcomes
-
Reduce wait times
-
Decentralize healthcare services, easing pressure on metro hospitals
Improved infrastructure in Tier-II and Tier-III cities also boosts accessibility for rural populations.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite strong progress, India still needs an estimated 2.4 million additional hospital beds to meet global standards. Gaps in infrastructure persist, but this also presents:
-
Significant opportunities for investment
-
Large-scale job creation
-
Scope for public-private collaborations
The focus remains on sustainable growth and developing a future-ready healthcare ecosystem.
Conclusion
India’s healthcare sector is in a dynamic phase of infrastructure expansion. With new hospitals, ICUs, emergency units, and advanced diagnostic technologies emerging nationwide, the country is moving toward a more resilient, equitable, and high-quality healthcare system, especially benefiting underserved regions.